- Do you know that the income you receive from leasing out your properties is also taxable? Many mistakenly think that rental income is tax-free, consequently incurring penalties for under-reporting.
EdgeProp February 22, 2024
We all know we need to pay taxes on the income we get from our vocations, be it as a hired worker, a gig worker or a self-employed businessman.
However, do you know that the income you receive from leasing out your properties is also taxable? Many mistakenly think that rental income is tax-free, consequently incurring penalties for under-reporting.
If you are a landlord, here is a guide that simplifies everything you need to know about filing a non-business income.
First of all, what is rental income tax?
It is a tax on profits you make from renting out residential and commercial properties, and even machinery and ships.
In a nutshell:
- It is filed under Section 4(d) of the Income Tax Act 1967.
- Residents are taxed from 0% to 30% based on a progressive rate of your rental income.
- Non-residents are subjected to a fixed tax rate of 30% on your rental income.
- The calculation starts from the first day your property is rented out.
- It is calculated based on net income (minus deductible expenses).
It’s important to differentiate between rental income and business income. Rental income falls under Section 4(d), while business income requires filing under Section 4(a).
Rental income is considered passive income, but if you actively manage your property (such as providing building maintenance, repairs of structural elements, cleaning services and installation of security systems), it could be classified as business income.
What are the deductible expenses?
To get your net taxable income, you are allowed deduct the following expenses incurred from upkeeping your rental property:
– Assessment tax
– Quit rent
– Property repairs
– Fire insurance
– Rent collection fee
– Rent renewal fee
– Interest on home loans
– Maintenance fee (strata properties)
If you have more than one property, you can group all the rental incomes and expenses together. Note that initial costs like advertising, legal fees, stamp duty and property agent commissions are considered non-deductible expenses.
Now, what happens if the rental property has been left vacant for a year with no income? You are not required to declare rental income of that property but the expenses incurred during that period can still be included as “deductible expenses”, which helps to offset your total net rental income if you have more than one property.
Here is an example of how you can calculate your net rental income.
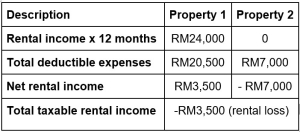
Your net rental income is your taxable income. If your net rental income is zero or you come up with a loss, you are not required to declare it as rental income in your tax filing.
Things to note in declaring your rental income
Failure to declare rental income or providing inaccurate information to tax authorities can result in penalties under Section 113 of the Income Tax Act 1967 (ITA). Penalties may include fines and special penalties equivalent to double the amount of undercharged tax.
1. Determine tax obligation: Before filing your income tax, you must determine if you meet the criteria for tax obligation. Individuals are eligible if your annual income after EPF (Employees Provident Fund) deduction exceeds RM34,000 or if you have been in Malaysia for at least 182 days within the year.
2. Calculate chargeable income: Calculate chargeable income based on the applicable tax rates and deductions. Keep records of all income sources, deductions, and receipts.
3. Filing period: Filing for income tax typically begins in the first quarter of the year for the previous Year of Assessment (YA). For example, in 2024, taxes for YA 2023 ending on Dec 31, 2023, will be filed.
4. Documents required: Keep pay slips, EA Forms and receipts as they are required for filing income tax.
5. File tax return: Income tax can be filed online via MyTax or manually at the Inland Revenue Board (Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri or LHDN) offices.
6. Deadline and penalties: Ensure taxes are filed before the deadline to avoid penalties. Late filing or misreporting earnings can result in penalties. If your income comes only from employment, the deadline is April 30 for manual filing and May 15 for e-filing. If you earn business income, the deadline is June 30 for manual filing and July 15 for e-filing.




